Introduction:
When it comes to managing renal failure, two primary forms of dialysis emerge as crucial
lifelines: Hemodialysis, commonly referred to as dialysis treatment, and Peritoneal Dialysis. Both
methods serve the vital function of removing waste and excess fluids from the body when the
kidneys are no longer able to perform this task. This article explores the pros and cons of these
two dialysis modalities, shedding light on the considerations patients and healthcare providers
must weigh in the decision-making process.
Dialysis Treatment:
Pros:
- Efficiency: Dialysis treatment is highly effective in quickly removing waste products and
excess fluids from the blood. The process is performed in a controlled medical environment,
ensuring precise management of the patient’s condition. - Widespread Availability: Hemodialysis centers are widely available, making this form of
treatment accessible to a larger population. Patients can receive care in a clinical setting, with
healthcare professionals overseeing the process. - Faster Sessions: Hemodialysis sessions typically last a few hours and are conducted a
few times a week, allowing patients to have more days off from treatment compared to
Peritoneal Dialysis, which often involves daily sessions.
Cons: - Rigid Schedule: Dialysis treatment requires strict adherence to a set schedule. This may
pose challenges for those with busy lifestyles or those who live in remote areas without easy
access to treatment centers. - Vascular Access Challenges: The need for a vascular access point, often in the form of a
surgically created arteriovenous fistula, graft, or catheter, poses a potential risk of infection or
complications.
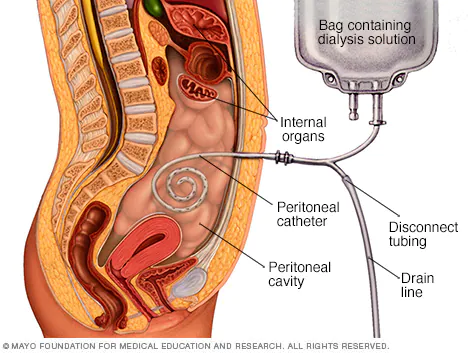
Peritoneal Dialysis:
Pros: - Flexibility: Peritoneal Dialysis offers greater flexibility as it can be performed at home.
Patients have the option to integrate dialysis into their daily routines, allowing for more
independence and reduced travel to treatment centers. - Gentler Fluid Removal: The gradual nature of fluid removal in Peritoneal Dialysis can
result in less stress on the cardiovascular system compared to the rapid fluid shifts in
hemodialysis. - Lower Impact on Blood Pressure: Peritoneal Dialysis is associated with a more gradual
decline in blood pressure during treatment, potentially reducing the risk of hypotension
compared to hemodialysis.
Cons:
Risk of Infection: The insertion of a catheter into the abdomen for Peritoneal Dialysis
creates a pathway for potential infections. Proper hygiene and adherence to sterile techniques
are crucial to mitigate this risk.
Time-Consuming Daily Sessions: Peritoneal Dialysis typically requires daily sessions,
which may be perceived as time-consuming. This can be challenging for individuals with busy
schedules or those who prefer a less frequent treatment approach.
Conclusion:
The choice between dialysis treatment and Peritoneal Dialysis is a significant decision in the
management of renal failure. Understanding the pros and cons of each modality is essential for
patients and healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans that align with individual needs,
preferences, and lifestyle considerations. Ultimately, the decision should be made
collaboratively, considering the unique circumstances and goals of each patient.